Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Peak Inverse Voltage Of Half Wave Rectifier Formula
Peak Inverse Voltage Of Half Wave Rectifier Formula. Where i m = i max which is equal to the peak instantaneous current across the load. And in your diode choice, i see you chosen 1n4004 and if.
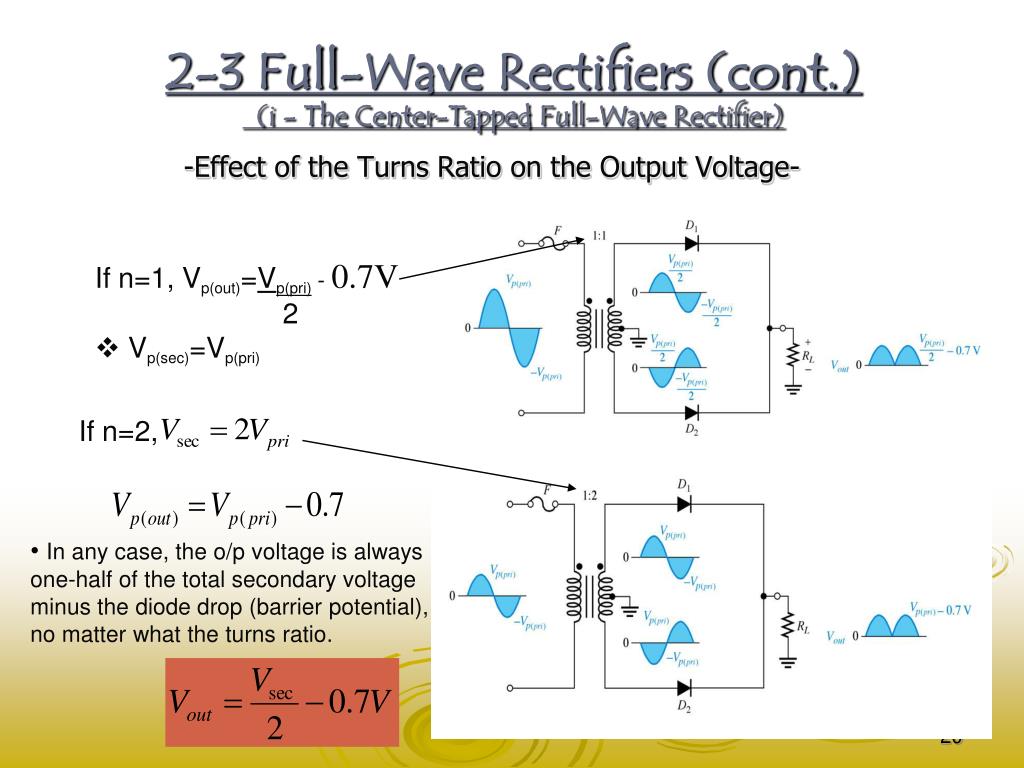
The peak inverse voltage of a full wave rectifier is double that of half wave rectifier. Average and peak currents in the diode. 0.7 0.7 i dd s v v v =+ =− + now, assuming that the source voltage is a sine wave v s =asin tω, we find that diode voltage is at it most negative
Hence The Rms Value Of The Load Current (I Rms) For A Half Wave Rectifier Is:
First, we recall that the voltage across the reverse biased ideal diodes was: The peak inverse voltage of a hwr is the maximum voltage that can a diode withstand without destruction when reverse bias is applied to it. Peak inverse voltage of half wave rectifier
Peak Inverse Voltage (Piv) | Half Wave Rectifier It Is The Maximum Reverse Voltage Which The Rectifier Is Required To Withstand During Nonconducting Period.
If the diode drop is neglected, the bridge rectifier requires. F) is that the magnitude relation between rms worth and average worth,. About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new.
C) Equal To The Input Voltage.
The peak inverse voltage of a full wave rectifier is double that of half wave rectifier. In half wave rectifier, piv equals v m , the peak value of applied voltage. In this diagram we can see the dc output vo from the diode produces a net average positive region above the axis, for the input full cycle, which can be determined by the formula:
Piv For Different Rectifiers Is Shown Below:
For full wave rectifier p i v = 2 e. Where i m = i max which is equal to the peak instantaneous current across the load. Since both the half cycles are conducted successfully.
In Full Wave Rectifier Peak Inverse Voltage Is Not Present.
For half wave rectifier p i v = e. Hence, the peak inverse voltage of diode in bridge rectifier is equal to the peak value of supply voltage. The maximum voltage across a reverse bias diode is known as peak inverse voltage.
Popular Posts
How To Connect Ammeter In Parallel Circuit
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment